How to Write a Play: Step-by-Step Guide 2025
Learn how to write a play with our 2025 step-by-step guide for students. Master playwriting structure, dialogue, and tips for academic success.
The process of analysis is crucial in so many aspects. Mainly in the academic world, it fosters a deeper understanding of complex concepts, helps in critical evaluation, and decision-making. The “how to analyze an informative speech” guide entails simplifying challenging information, analyzing the aspects, and making informed conclusions. Analysis of an informative speech entails a study of how adequately it presented information to the audience. That involves the evaluation of the clarity of the speaker, organization, evidence usage, and delivery. Some significant factors worth getting into consideration are the aim of the speaker, the intended audience, the effectiveness of his arguments, and, in general, his effect on the hearer.
The major aim of analysing an informative speech is to examine how well the speaker is able to transmit information and how efficiently the audience also receives and appreciates the same. Before you know the process of analyzing the speech, knowing how such analysis makes students, educators, and professionals efficient in their public speaking skills is essential. During the process of evaluating content, structure, delivery, and impact of the informative speech, they learn how to present a speech on stage in front of the audience.
A critical analysis of an informative speech entails the review of the effectiveness of the speech in educating the listeners. It entails a number of major domains, such as the purpose of the speaker is to inform well. Second, an assessment of whether the speech was well-adapted to the audience based on prior knowledge and interests. Third, critically reading through the material and analyzing its format to ensure that the information was correct and supported. Lastly, evaluating how the speaker delivered their ideas, including talk, vocal tone, body language, and other visual aids, to determine whether these approaches made their message easy to understand.
When it comes to how to analyze an informative speech, it is a fundamental classroom task in the education field, training learners on the skills of being critical listeners and communicating well. It is how judges measure who is right or wrong in matters of exhibiting factual coherence, arrangement, and presentation of cases in competitions such as debate. At the workplace, it can aid in the creation of effective presentations, the evaluation of reports by workmates, and the provision of clear and precise information in decision-making.
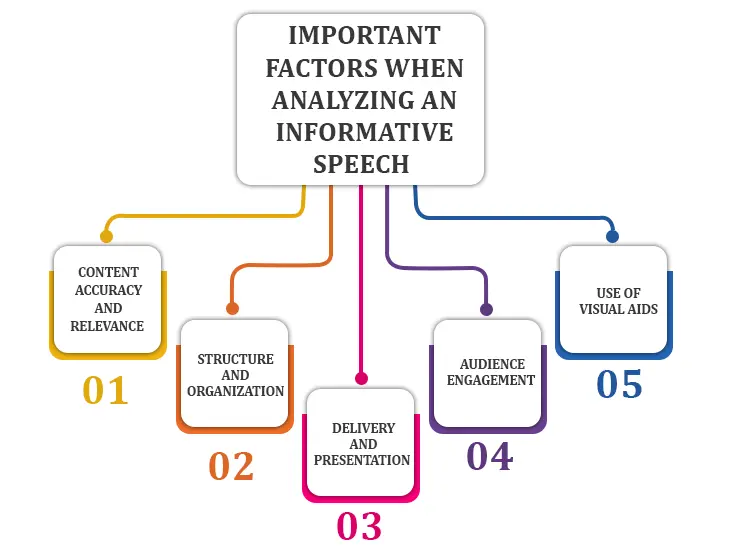
Analyzing an informative speech is not merely listening, but rather an organized assessment of how well a speaker presents information. It implies breaking down the content, structure, and layout to reach the audience and make a real sense of the presentation. The most important criteria help in identifying what is good and what needs improvement in the process of sharing knowledge.
This criterion evaluates the accurate nature of the information given. A proper informative speech is supported by precise research that can be proved. Included in the analysis is determining whether the sources can be trusted and whether such sources clearly support the intent of the speech. Relevance is another crucial point; the content should be relevant to the topic as well as the needs/interests of the audience.
Another factor in the criteria for analyzing an informative speech is that a structured informative speech leads the audience through the content without difficulties. The criterion under consideration is the clarity of the introduction, comprising the statement of the thesis and providing a preview of the work, the logical order of the main statements, the strength of tracing the connection between ideas, and the quality of the conclusion. An easy organizational scheme improves the understanding and remembering of information.
This examines the method that is used by the speaker for their speech. The main factors involve projection using volume, rate, clarity, tone, and eagerness. Some of these non-verbal cues are: eye contact, gestures, postures, and facial expressions. It is then essential to know that effective delivery helps in making the message heard, understood, and keeps the interest of the audience without interfering with the content.
The success of an informative speech is usually determined by how well the speech reaches the audience. This standard assesses the way in which the speaker was able to grasp the interest of the listeners and also hold it. Such forms of analysis could be how rhetorical questions are utilized, how the examples of informative speech analysis seem relatable to the listeners, how the speaker shows a narration, or how they work with interactive features or change the speech in accordance with the reaction of the audience.
When present, the visual aids must complement rather than distract from the informative message. They analyze them, including their design that involves their clarity, readability, and good looks, and their relevance to the content in which they were seamlessly incorporated into the speech. Are they used to reduce the complexity of a message, to demonstrate important points, and to actually reinforce the message of the speaker, or are they just decorations that only distract?
Analyzing an Informative Speech involves a set of things and a process that is essential to be followed. You must always consider a set of criteria for analyzing an informative speech and a step-by-step guide, so the speech can easily be analyzed:
To analyze an informative speech successfully, you should start with an understanding of its central purpose. This is finding out the intended message by the speaker and to whom.
After understanding the purpose of the speech, delve into the content of the message. See how well the information is presented and whether it is accurate, clear, and relevant to its targeted audience:
A developed speech helps the audience to follow the message. Answer the packaging of the ideas by the speaker:
The way such a speaker presents his/her information is quite significant as far as effectiveness is concerned. Pay attention to such details as voice, gestures, and the overall involvement.
The last step to how to evaluate an informative speech will be to provide helpful information to the speaker. Present objective and fair evaluative comments to a learner, bringing out the positive and pointing out effective ways to learn or get better:
| Step | Description | Key Questions |
| 1. Identify Purpose | Understand if the speech is meant to inform, not persuade, or entertain. | What is the primary intent of the speech? |
| 2. Analyze Audience | Determine the target audience and the relevance of the topic to them. | Who is the speech directed at? Why should they be interested? |
| 3. Examine Structure | Review the organization: introduction, body, conclusion. | Are the main points clear and logically ordered? |
| 4. Evaluate Content | Assess the use of facts, statistics, examples, definitions, or expert testimony. | Does the speech rely on verifiable evidence? Are the examples and supporting details relevant? |
| 5. Assess Delivery | Observe vocal quality, body language, visual aids, and overall engagement. | Does the speaker speak clearly, connect with the audience, and use visuals effectively? |
| 6. Check Objectivity | Confirm that the presenter remains neutral and avoids persuasive tactics or opinions. | Is the information unbiased and clearly attributed? |
| 7. Judge Effectiveness | Evaluate whether the speech increased understanding or provided useful knowledge. | Did the audience learn something new? Was the purpose achieved? |
Analysis of speeches encompasses the consideration of content and structure, delivery, and audience appreciation, among others. With the help of rubrics and other tools, you will be able to receive an objective understanding of your strengths and areas to improve.
A rubric is a scoring guide applied in evaluating performance depending on the specified criteria. A rubric can be used to assess many elements of a presentation made through speech, allowing an objective assessment of it. Something like this is a rough process of composing one:l
Other than subjective rubrics in the process of how to critique an informative speech, there are various tools that can support speech analysis, delivering more objective information. These may include mere recording devices to advanced software.
Audio/Video Recording Devices: They are essential in the recording of a speech, as one can replay it. They allow observing the presentation's verbal and non-verbal details in detail.
Speech-to-Text Software: This software is used to convert spoken words into text format. It is priceless to be used to analyze the vocabulary, define the presence of filler words, and see whether the grammar is usable or not.
Voice Analysis Software: Such special applications can thoroughly examine speech acoustically. They quantify such aspects of voice as pitch, volume, and rate of speaking; they provide objective information about the voice features.
Audience Polling/Feedback Tools: Audience polling/feedback tools enable one to collect real-time feedback and perceptions of the audience towards a speech. They assist in determining the understanding, interest, and general impact on the listeners.
Timer: a basic but vital instrument in controlling the time of a speech. It assists in making sure that the speaker keeps to the set periods of time and maintains an appropriate pace.
To analyse an informative speech, we have picked one of the famous informative speeches, “I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King Jr.
Read the Complete Speech Here (PDF): “I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King Jr. (1963)
| Category | Excellent (4) | Good (3) | Fair (2) | Needs Improvement (1) |
| Content & Understanding | Demonstrates deep and accurate understanding of the speech’s key themes, context, and purpose. | Shows a clear understanding but may miss minor details. | Presents a basic understanding; some major points are incomplete. | Shows little understanding; key themes or context are missing. |
| Organization | Analysis is logically structured with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. | Mostly organized with minor lapses in coherence or flow. | Organization is weak; information is presented out of order. | Lacks clear organization; ideas are confusing or jumbled. |
| Use of Evidence | Supports analysis with well-chosen quotes/examples from the speech, properly cited. | Uses relevant examples, but some may be less specific or less effectively cited. | Few examples/quotes used, or citation is inconsistent. | Lacks textual evidence; relies on summary/opinion. |
| Rhetorical Devices | Accurately identifies and explains at least three rhetorical devices (e.g., repetition, metaphor, allusion). | Identifies at least two devices and provides some explanation. | Identifies one device, but the explanation is unclear or incorrect. | Does not identify or explain rhetorical devices. |
| Impact and Significance | Insightfully explains the speech’s historical and social impact, relating it to the Civil Rights Movement. | Discusses impact but with less detail or depth. | Provides a basic or vague discussion of significance. | Fails to address impact/significance. |
| Language & Mechanics | Writing is clear, engaging, and error-free. Language is academic and precise. | Minor errors, but overall clear and appropriate. | Noticeable errors in grammar or mechanics; language is basic. | Frequent errors: writing is unclear or complicated to follow. |
| Speech | Speaker | PDF Link | Key Analysis Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| “I Am Prepared to Die” | Nelson Mandela | View Full PDF Analysis |
|
| Speech | Speaker | PDF Link | Key Analysis Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| “Gettysburg Address” | Abraham Lincoln | View Full PDF Analysis |
|
| Speech | Speaker | PDF Link | Key Analysis Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| “We Shall Fight on the Beaches” | Winston Churchill | View Full PDF Analysis |
|
| Speech | Speaker | PDF Link | Key Analysis Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| “Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death” | Patrick Henry | View Full PDF Analysis |
|
The frequent pitfall of informative speeches is that:
Growth runs on effective feedback, and tips for constructive feedback are as follows:
You can use a variety of resources during the how to evaluate an informative speech. Books on rhetoric and on public speaking may be found in libraries. The expert advice is given by the professors teaching communication or English. The peers also provide desirable new ideas and practice exposure. Moreover, there are websites such as TED Talks, educational websites, and speech analyzer tools, which may give various illustrations and models of further knowledge.
It can only be after making a good analysis of an informative presentation that one realizes the effectiveness of a presentation. Through the study of clarity, organization, audience outreach, and presentation, one may identify the strong suits and areas to be improved. This analysis is crucial in developing skills in communicating so that information is not merely given, but is actually absorbed and comprehended by the target audience.
When analyzing an informative speech, some of the important factors are determining the purpose of the speaker. You check on the accuracy of the contents, the relevancy of the contents with the audience, the clear structure and organization of the speech, and the effectiveness of the delivery and presentation.
Informative speech promotes knowledge in an effective manner. Such aspects as properly researched, topical content, logical and explicit organization, and active presentation are essential. The presenter has to cater to the needs of the audience, employ simple language, and incorporate visual materials effectively to increase the level of comprehension and memorization.
In critiquing an informative speech, the evaluator looks at the clarity, accuracy, and the general impact of the speech. Your judgments are based on the success with which the speaker sought to inform, the reasoning behind the content, and how well they deliver. The interactivity with the audience and the usefulness of any graphic material also play a vital role.
In order to determine whether an outline of the informative speech is good enough or how to assess an informative speech outline, make sure that it has a determined purpose and a thesis statement. Ensure there is logic in the arrangement of main points and sub-points, flowing reasonably with a supporting argument. Determine whether the transitions exist, work, and whether the introduction and the conclusion play their roles in introducing and summarizing the information.
Subscribe now!
To our newsletter for latest and best offers