How to Write a Play: Step-by-Step Guide 2025
Learn how to write a play with our 2025 step-by-step guide for students. Master playwriting structure, dialogue, and tips for academic success.
Lincoln-Douglas Debates created history when they happened. Enter the arena in which intellect is the sword and morality the shield, the world of Lincoln-Douglas debate. It is called the lincoln douglas debate format because it is the name of a series of seven debates between Abraham Lincoln and Stephen Douglas, which took place in 1858 in a thoroughly philosophical conflict of competing values. Think of a fast-paced, high-stakes debate, and every word counts, so the debaters are not only trying to win but also trying to find out the core truths of our society. This guide, which I have developed on your behalf, will shine some light on the path, with the format of the rules, where the rules of engagement are critical, and in a final glance, at the ethically rich issues that form the foundation of LD. You are either a beginner who wants to know how to survive or an expert who wants to gain a tactical advantage. Get ready to learn how to play the one-on-one philosophical duel.
But when it comes to modern times, it is just a debate that must be done between two people, which is mainly called the “one-on-one” debate. In this debate, no other partners will be required as it is not between the team or two to three people. Let’s delve more into this and learn about these debates.
Lincoln-Douglas Debate is a one-on-one debate that deals with moral, philosophical, and ethical issues, sometimes known as a value debate. It is so called because it refers to the historic debates in 1858 between Abraham Lincoln and Stephen Douglas 1858 regarding the issue of slavery and popular sovereignty. LD is used in the contemporary world as an intellectual laboratory for students. Debaters do not only discuss what is practical but also what is right according to complexity, i.e., what should be the case, e.g., justice, liberty, and equality. It is an educational lincoln douglas debate format that supports in-depth research, critical thinking, and high-level speaking, and prepares participants to wrestle with the most underlying and polarizing problems in society.
The lincoln douglas debate is a one-on-one debate that is based on philosophical and moral issues. Each round is a timed format with the affirmative and the negative speakers taking turns to present and refute the points. Before going ahead, you can explore the Complete Guide to Debates with types, formats, and structures to understand Debates clearly.
| Order | Speech Name | Speaker | Duration | Purpose |
| 1AC (1st Affirmative Constructive) | Affirmative | 6 minutes | Present the case in support of the resolution, including the value framework and contentions. | |
| Cross-Examination 1 | Negative | 3 minutes | Question and clarify affirmative arguments to expose weaknesses or gain admissions. | |
| 1NC (1st Negative Constructive) | Negative | 7 minutes | Challenge affirmative case; present negative case, including refutations and contentions. | |
| Cross-Examination 2 | Affirmative | 3 minutes | Question and clarify negative arguments. | |
| 1AR (1st Affirmative Rebuttal) | Affirmative | 4 minutes | Respond to negative arguments and reinforce affirmative case points. | |
| 2NR (2nd Negative Rebuttal) | Negative | 6 minutes | Respond to affirmative rebuttals, further refute the affirmative case, and strengthen the negative. | |
| 2AR (2nd Affirmative Rebuttal, Final Focus) | Affirmative | 3 minutes | Final summary emphasizing the key reasons why affirmative should win the round. |
The Prep time, also known as preparation time is extremely crucial to learn How to Debate Efficiently, and it definitely is a vital strategic resource during a Lincoln-Douglas (LD) debate round.
After answering what is lincoln douglas debate that is a one-on-one competitive mode that is uncharacteristic of itself with excessive focus on ethics and philosophy. It can be referred to as a value debate since all of the structures of the case are constructed based on a philosophical framework, which determines how the judge is expected to view the resolution. This intellectual framework is divided into two main components, which are the Framework (Value Premise and Value Criterion) and the Contentions. The crucial link here is that the arguments need to show how you, in the resolution, are the side that gives the Value at the best of the Criterion.
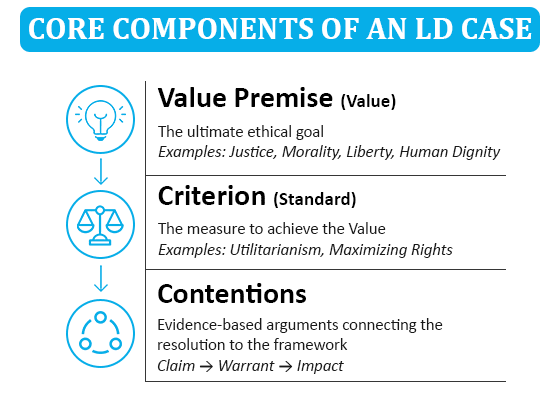
The abstract, ultimate ethical goal, which the debater intends to hold on to or accomplish during the resolution of the debate, is the Value Premise or the Value. It is the utmost ideal in both the priority in the round.
The Standard, or the Value Criterion, is the concrete philosophical act or measuring rod, applied to accomplish, gauge, or rank the Value Premise. It becomes the way through which the judge considers the debates in the round.
The Contentions refer to the specific, subject-related argument that involves facts, evidence, and logical arguments to demonstrate that your half of the resolution is able to connect and support the philosophical framework (Value and Criterion).
The National Speech & Debate Association (NSDA) and the National Christian Forensics and Communications Association (NCFCA) have also published their official lincoln douglas debate topics as of the 2025-2026 school year. The NSDA changes topics every two months, whereas NCFSA has only one resolution throughout the whole competition.
NSDA applies diverse resolutions of ethical or policy-oriented nature to its Lincoln-Douglas (LD) events of debate. The subject matter is different every two months during the season, and in the National Tournament, there is another resolution.
| Cycle | Dates | Resolution Options |
| September/October 2025 | Released August 1 | Resolved: In the United States criminal justice system, plea bargaining is just. Resolved: In the United States, the use of artificial intelligence technology in the criminal justice system is immoral. |
| November/December 2025 | Released October 1 | Resolved: The United States ought to prioritize green growth over degrowth. Resolved: The United States ought to rewild substantial tracts of land. |
| January/February 2026 | Released December 1 | Resolved: The possession of nuclear weapons is immoral. Resolved: On balance, geoengineering is moral. |
| March/April 2026 | Released February 1 | Resolved: The use of economic sanctions by the United States is immoral. Resolved: The United States military ought to abide by the principle of non-intervention. |
| National Tournament 2026 | Released May 1 | Resolved: Wealthy countries have a moral obligation to provide development assistance to other countries. Resolved: Democracies ought to prioritize the protection of civil liberties over national security. |
This resolution asks debaters to think about a fundamental philosophical and moral obligation question about the future of humanity in the last frontier. Instead of whether we should explore space, the argument is now about how we should control and use resources there, since technology makes space easier to get to.
| Organization | Resolution |
| NCFCA | Resolved: In the exploration and utilization of outer space, international cooperation should be prioritized. |
The lincoln douglas debate is a highly competitive, rapid speech event that is a popular high school-level event. The format is different in that it puts almost all attention on moral and philosophical questions that are brought up in a resolution, instead of individual government policies. The key to the success of a debater is his or her capacity for sound philosophical reasoning and practical communication skills in a rigid and alternating speech pattern.
The criteria used to evaluate an LD debate revolve around which participant of the debate is more effective in solving the philosophical conflict that is involved in the resolution, a factor usually informed by the Value Framework in which the competing parties are based. The key ruling is grounded in an organized comparison whereby the judge has to initially decide on which Value and Value Criterion is to be put into consideration and then decide upon which debater has the best arguments meeting that criterion:
The philosophical lens, the Framework of Value, and the Value Criterion are what delineate the range of the debate and offer a rule of decision to the judge. This framework is necessary since value-based resolutions must have a criterion to balance opposing moral duties and possible consequences. With the clear structure, the debaters present the most significant end, ultimate, and give a definite way of how the arguments by each should best meet the end.
The discussion centered on the basics of Lincoln-Douglas (LD) debate, which is a one-on-one competition event that is based on philosophical resolutions. The main aim of LD is to maintain a high moral thing, such as Justice or Liberty, against your opponent. Such a lincoln douglas debate format is very different from the Policy debate, which entails narrowly targeted actions of the government and in-depth evidence. Finally, LD enhances the ability to think critically and argue by making debaters aware of opposing ethical principles and enabling them to state them.
The Competitive debate is mainly aimed at proving philosophically that something is true or false. This is done by showing that your side, the one you are assigned to, more complies with a particular and high value of morality like Justice or Liberty. The debater is supposed to persuade the judge that his or her case has the strongest moral argument on the resolution.
The shared values debate serves as the final objective of a case. The popular philosophical principles are Justice, which is often characterized by a certain parameter, such as adherence to human rights, and Liberty or Individualism, the maximization of personal freedom. Morality, Societal Welfare, and Dignity are other common values.
LD debate is a two-person debate that is based on ethical and philosophical values. Policy debate is on a two-on-two lincoln douglas debate format that focuses on the plans of the government or certain policies. Policy generally demands much more empirical evidence and delving into technical specifics.
In addition to the case structure, the very activity is an essential source of learning. It is an effective device for critical thinking development as it compels the involved participants to examine the complex ethical dilemmas in two ways. The LD also has a drastic effect on the development of speaking skills in public, argumentation abilities, and philosophical literacy.
Subscribe now!
To our newsletter for latest and best offers